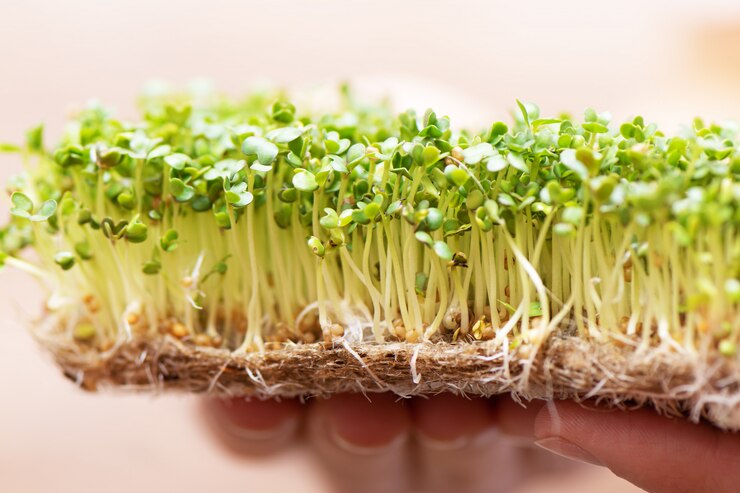
Sprouts are the young shoots grown from the seeds of various plants. They are typically grown from legumes, grains, and seeds such as mung beans, alfalfa, lentils, broccoli, and wheat. Sprouting enhances the nutritional content of the seeds and makes them easier to digest. Today we are going to describe the health benefits of sprouts and its nutritional chart.
How to Make Sprouts at Home
Making sprouts is simple:
- Choose Seeds: Select high-quality seeds such as mung beans, chickpeas, or alfalfa.
- Soak: Rinse the seeds thoroughly and soak them in water overnight (6-12 hours).
- Drain: The next morning, drain the water and rinse the seeds.
- Store: Place the soaked seeds in a sprouting jar or container. Ensure they are in a warm, dry place away from direct sunlight.
- Rinse Daily: Rinse the seeds twice a day with fresh water, draining after each rinse.
- Harvest: In 3-5 days, once small shoots have appeared, your sprouts are ready to eat.

How and When to Consume Sprouts for Better health benefits of sprouts
- Morning: Consuming sprouts as part of your breakfast can provide a healthy, energy-boosting starting to the day. Add them to salads, smoothies or sprinkle them on toast.
- Pre-Workout: Sprouts are an excellent snack before a workout due to their high protein and energy content.
- As Snacks: Enjoy sprouts as a mid-morning or afternoon snack to curb your hunger while getting a nutritional boost.
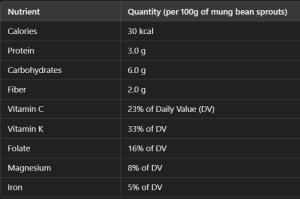
Nutritional Value of Sprouts
Sprouts are packed with essential vitamins, minerals, antioxidants, and protein. Here’s a look at their nutritional content:
Health Benefits of Sprouts
- Nutrient-rich: They are rich in many vitamins (like vitamin C, vitamin A and vitamin K), some minerals (e.g., phosphorus, iron, magnesium) and antioxidants that make them a healthy ingredient in our bodies.
- Improves Digestion: During sprouting, it releases many simple sugars hence easier to digest as compared with unsprouted grains and legumes. In addition, they have high fiber content, which ensures good digestion.
- Boosts Immunity: These vegetables contain high amounts of vitamin C as well as some different antioxidants that strengthen human immunity and protect from harmful components called free radicals.
- Weight Loss: Despite containing few calories but being rich in both proteins and dietary fiber, sprouts make a person feel full for extended periods hence reduce unnecessary intakes of foods that can lead to weight gain.
- Supports Heart Health: Sprouts are good for our hearts, by helping lower bad cholesterol (LDL) and increasing good cholesterol (HDL).
- Enhances metabolism: Sprouts enhances metabolism due to the presence of enzymes which help the body absorb nutrients more efficiently.
- Improves Blood Sugar Levels: Sprouts improve blood sugar levels which is helpful particularly when it comes to prevention of sugar spikes among diabetic patients.
- Skin and Hair Health: Nutrients such as vitamin C facilitate the production of collagen aiding healthier skin and hair as well as antioxidants that fight against free radicals in the body to prevent aging effects.
- Bone Health: Sprouts with calcium, magnesium and vitamin K support strong bones.
Other Health Benefits of Sprouts
- Detoxifies the Body: The high amount of fiber in sprouts act as a cleaner of the digestive system by removing toxins from it thus allow for general detoxification
- Energy Boost: The rich nutrient make-up of sprouts serve as an accelerant and one can use them before exercises or a snack.
- Mental Clarity: It maintains the brain alert because they are endowed with vitamins and minerals such as B complex which enhances brain activities like concentration mental clarity.

How Much Sprouts Should You Eat?
Daily Intake: In general, 1 cup or roughly 100g of raw sprouts is a common portion size. They are easy to sprinkle over a salad, sandwich, smoothie or even take alone as a snack.
Portion Control: There is no doubt that sprouts contain fewer calories, but they should be taken in moderation because of the risks associated with overconsumption of dietary fiber which may lead to digestive problems.
When to Avoid Sprouts
Despite their high nutritional value, if not washed properly and stored raw sprouts may have germs such as E.coli bacteria or Salmonella bacteria. To avoid this:
- Make sure that you rinse them thoroughly before consuming.
- If there is any concern, think about lightly steaming or cooking sprouts in order to kill probable germs.
Sprouts for Weight Gain vs. Weight Loss
- When gaining weight, you can pair nuts, seeds, or some other fatty oils with sprouts for extra calories.
- Sprouts are low in calories and high in essential nutrients for weight loss. To keep full and avoid overeating, you could include them in salads or eat sprouts like a snack.
To get more information about herbal and health benefits of fruits, vegetables and nutrition tips please visit HerbalGourmets website.






















